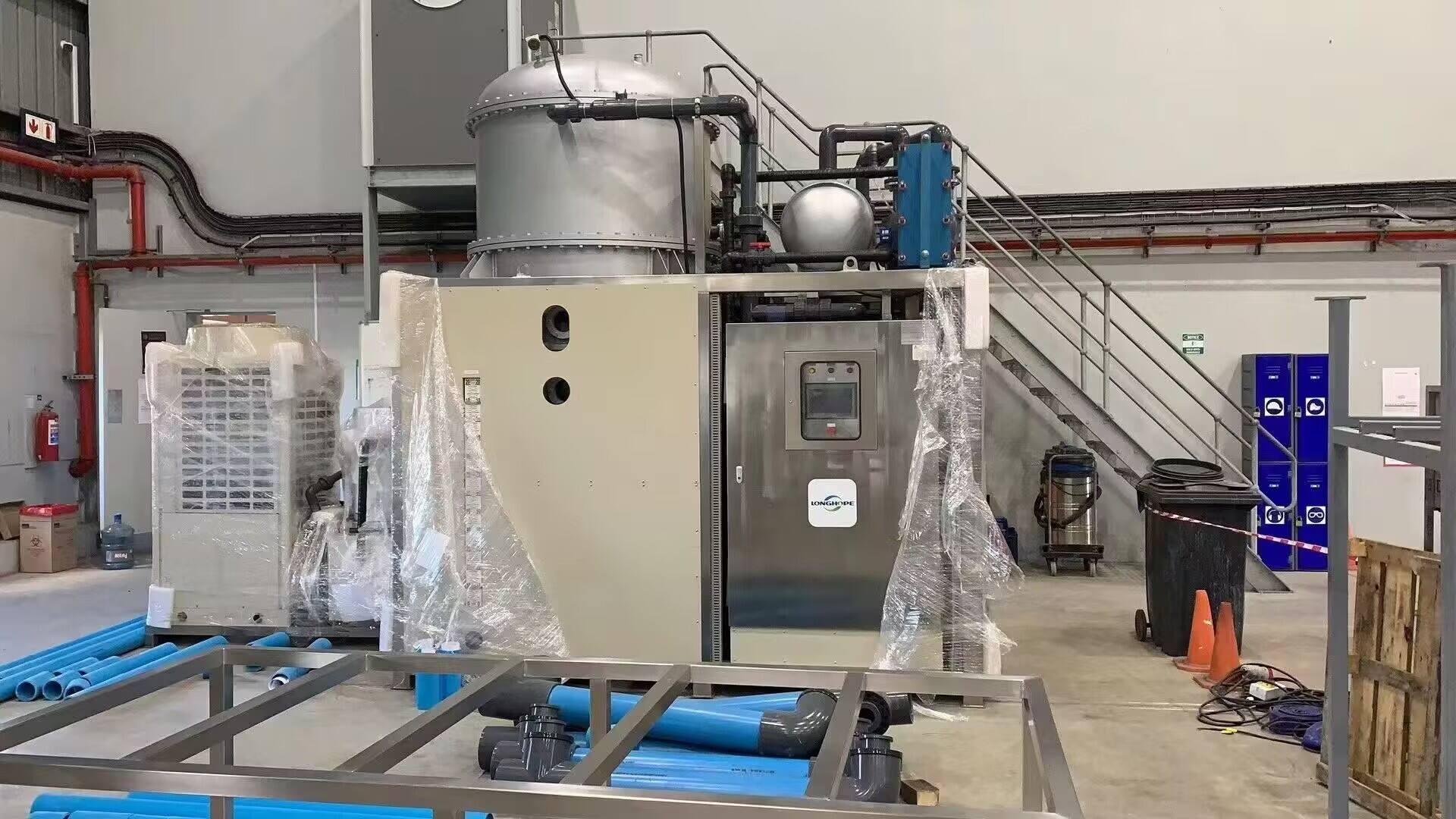
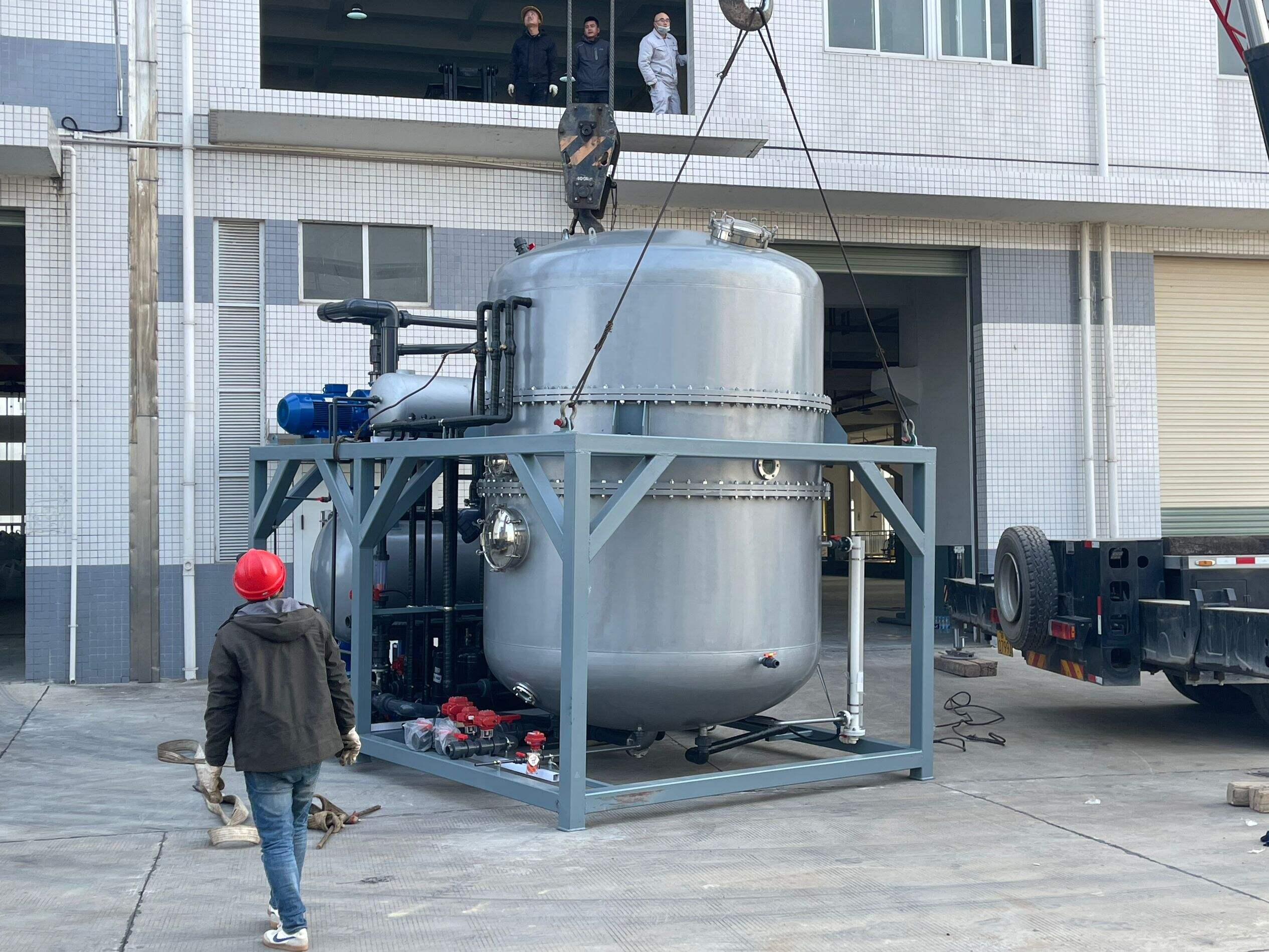
evaporator in refrigeration system
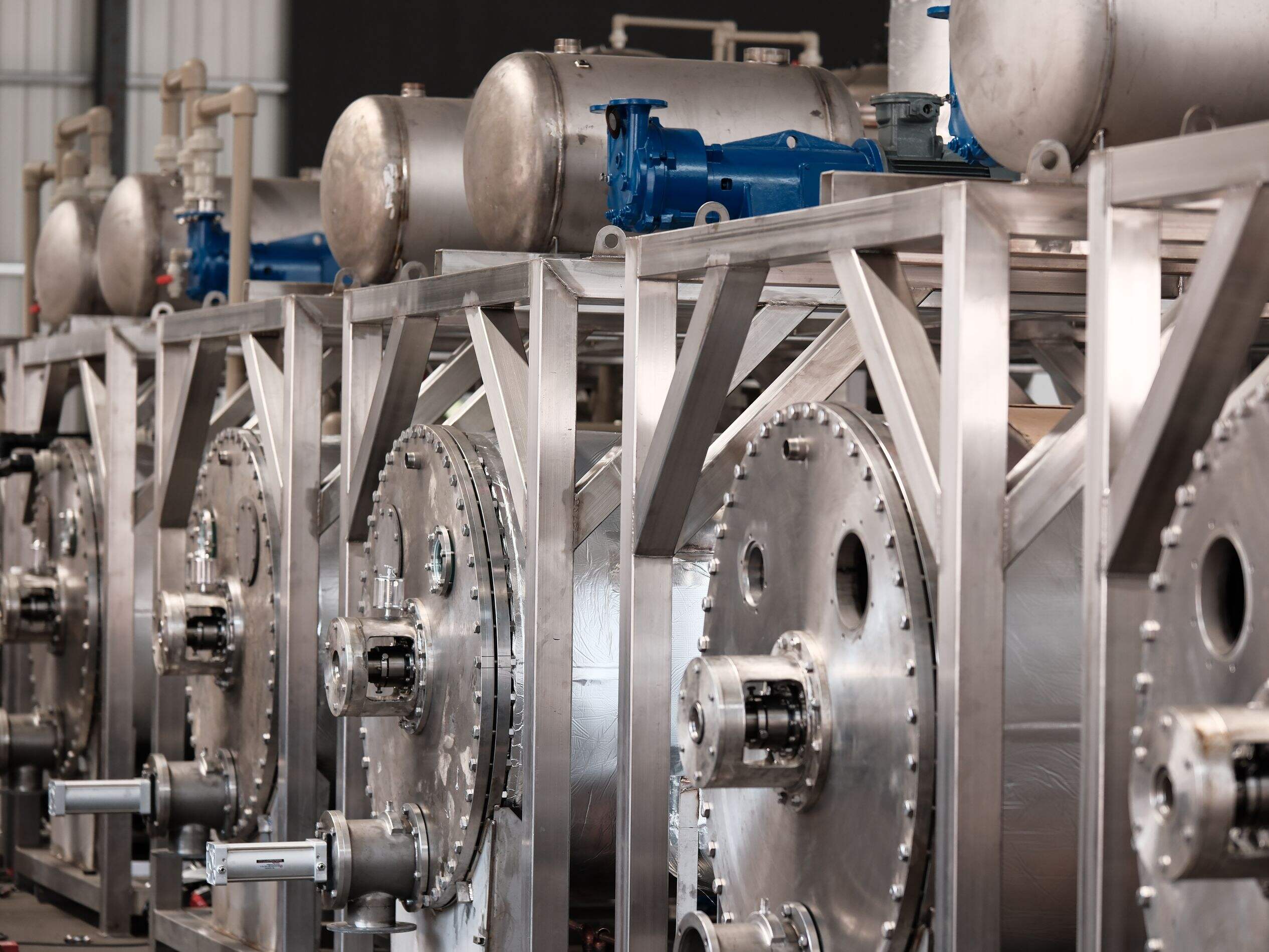
The evaporator is a crucial component in refrigeration systems, serving as the primary heat exchange device where the actual cooling process occurs. This vital component operates by allowing the refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding space or substance that requires cooling. Inside the evaporator, the liquid refrigerant changes state into a gas through the process of evaporation, effectively removing heat from the environment. Modern evaporators are designed with advanced heat transfer surfaces, typically consisting of specialized fin and tube arrangements that maximize thermal efficiency. These components are carefully engineered to maintain optimal temperature control while ensuring energy efficiency throughout the cooling process. The evaporator's design can vary significantly based on specific applications, ranging from industrial cold storage facilities to residential air conditioning systems. The component features various configurations including shell and tube, plate type, and finned tube designs, each optimized for specific cooling requirements. In commercial and industrial applications, evaporators often incorporate sophisticated defrost systems and precise temperature control mechanisms to maintain consistent performance. The technology continues to evolve with innovations in materials and design, leading to improved heat transfer coefficients and enhanced overall system efficiency.